Common Misconceptions About TSCM Bug Sweeping Equipment
In today’s business environment, protecting meeting privacy and preventing information leaks has become a priority for many companies & organization. Many end users are often confused with various bug sweeping equipment due to less technology knowledge on specialized terminology. This article will clarify several common misconceptions about bug sweeping equipment to help you make more informed security decisions.
Before start, let’s make a comparison of Surveillance Countermeasure Terminology
Generally speaking, to most users, when we talk about bug sweeping equipment, it is common referring to counter-surveillance equipment.
| Term | Definition Scope | Primary Applications | Expertise Level | Example Equipment |
| TSCM Equipment | Technical Surveillance Countermeasures – highest-level professional anti-espionage tools | Government/military facilities, diplomatic sites, corporate R&D centers | ★★★★★★ (Military/Gov) | Spectrum analyzers, advanced NLJDs, laser eavesdropping detection systems |
| Counter-surveillance Equipment | Broad-range anti-surveillance solutions covering prevention and detection | Corporate security, executive protection, privacy-sensitive environments | ★★★★★ | RF detectors, GPS jammers, anti-tracking systems, non linear junction detectors |
| Bug Sweeping Equipment | Specialized tools for detecting hidden surveillance devices (focused on scanning) | Temporary meeting spaces, hotel rooms, vehicle inspections | ★★★★ | Portable RF scanners, thermal cameras, non-linear junction detectors |
| Anti-eavesdropping Equipment | Audio-focused protection against listening devices | Boardrooms, legal offices, healthcare privacy areas | ★★★☆ | Ultrasonic jammers, white noise generators, telephone line encryptors |
1. Wireless Signal Detectors vs. Wireless Signal Analyzers
Although both devices are commonly referred to as “signal detectors,” they have significant differences in functionality and application scenarios:
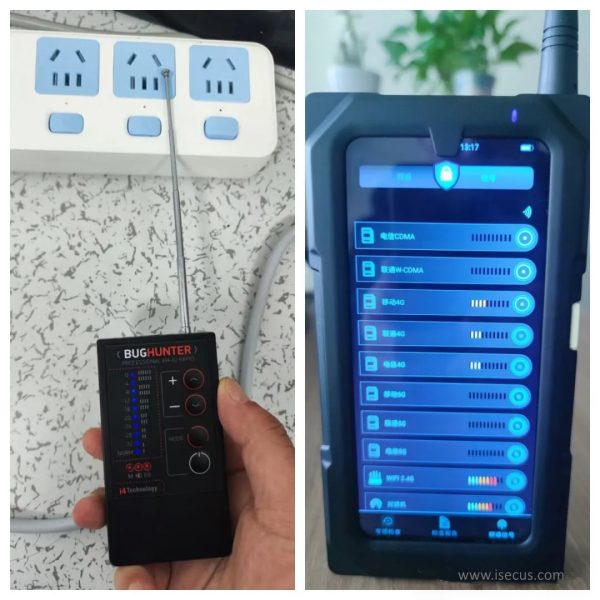
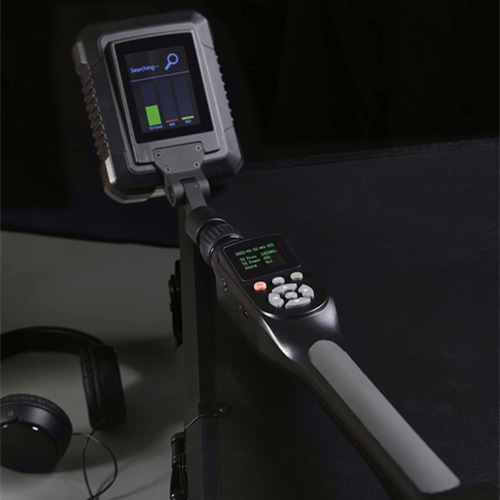
Wireless Signal Detectors (Near-field Signal Detectors)
- Core Feature: Uses directional antennas, also known as “field strength meters”
- Main Function: Precisely locates signal emission sources
- Positioning Accuracy: High precision, can pinpoint signal sources within a 3cm range even in noisy environments
- Use Case: When you need to find the exact location of hidden listening devices
Wireless Signal Analyzers
- Core Feature: Uses omnidirectional antennas, providing all-around signal scanning
- Main Function: Analyzes various signals in the environment, helping to identify abnormal signals
- Positioning Accuracy: Lower, cannot precisely pinpoint specific locations
- Use Case: Conducting comprehensive signal environment assessments of meeting rooms
When choosing these kind of Bug Sweeping equipment: You need to confirm whether suspicious signals exist in the environment or not. If not, then select a wireless signal analyzer; if you’ve already confirmed suspicious signals and need to locate them precisely, choose a wireless signal detector. The ideal approach is to use both in combination—first scan with an analyzer, then precisely locate with a detector.
2. Professional Wireless Signal Spectrum Analyzer VS Industrial Spectrum Analyzer VS Wireless Signal Analyzer
Spectrum analyzers are important tools in anti-surveillance work, but there 3 different types of TSCM equipment are often confused by non-professional customers in the market:
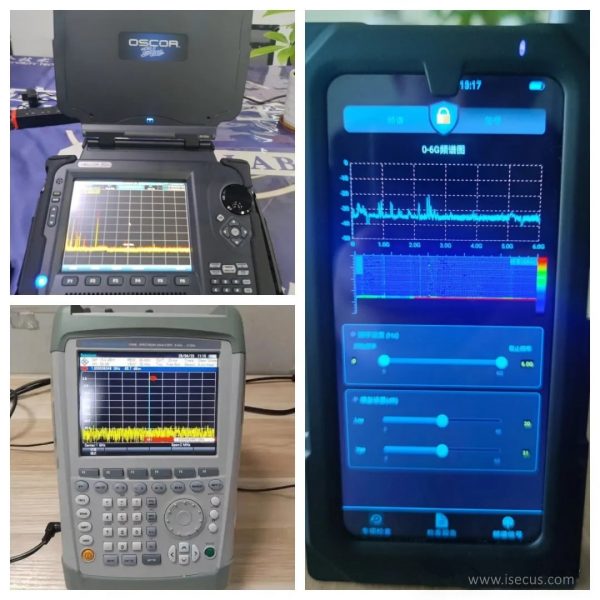
Professional Wireless Signal Spectrum Analyzer
- Positioning: Semi-professional detection equipment in the anti-surveillance field
- Price: Expensive, but optimized for anti-surveillance needs
- Frequency Range: Available in various frequency ranges: 6G/8G/9G/12G/18G/24G/40G and more
- Unique Functions:
- Audio and video signal demodulation
- Abnormal signal diagnostics
- FM signal tracking
- Optimized signal recording and comparison functions
- Some models include line detection capabilities
Typical models are Oscar Signal Spectrum Analayzer from REI in USA.
Industrial Spectrum Analyzer
- Positioning: Belongs to the instrument and meter category
- Characteristics: Focuses on signal transmission and reception testing
- Price: Most models are less expensive than professional analyzers, but high-end models can be more expensive
- Use Case: RF equipment testing, can also be used for basic anti-surveillance work
Wireless Signal Analyzer
- Positioning: Comprehensive signal detection and analysis equipment
- Size: Compact and portable, mostly handheld designs
- Functions: Simplified spectrum functionality, retaining background signal recording, comparison, and audio/video demodulation functions
- Use Case: Quick on-site detection, security checks for non-fixed locations
Typical models are BugHunter‘s portable signal analyzer.
When selecting a spectrum analyzer to sweep bug, please consider your professional level, budget, and actual needs. For corporate security departments, professional analyzers may be appropriate; for small and medium-sized enterprises with limited budgets, portable analyzers might be a more practical choice.
3. Non-Linear Junction Detector VS Wireless Signal Analyzer
Nonlinear junction detectors are fundamentally different from other signal detection devices, and many people mistakenly confuse them with wireless signal analyzers:
Non-Linear Junction Detectors
- Working Principle: Actively emits signals to detect whether items contain metal, metal oxide, or semiconductor components
- Unique Feature: It is the only device among all passive detection equipment that actively emits signals
- Use Case: Examining items that don’t normally contain metal, such as pictures, tissue boxes, books, ornaments,woods,
- Operation Precautions: Avoid using with other signal detection equipment simultaneously to prevent interference
The specific functions of the wireless signal analyzer have been introduced above and will not be repeated here.
Practical Application Value
As a significant TSCM equipment , NLJD detectors can discover miniature electronic devices that are difficult to detect with ordinary metal detectors, especially listening devices hidden inside non-metallic objects. No matter the electronic devices are power on or off. This is one of the essential tools for ensuring complete meeting room security.
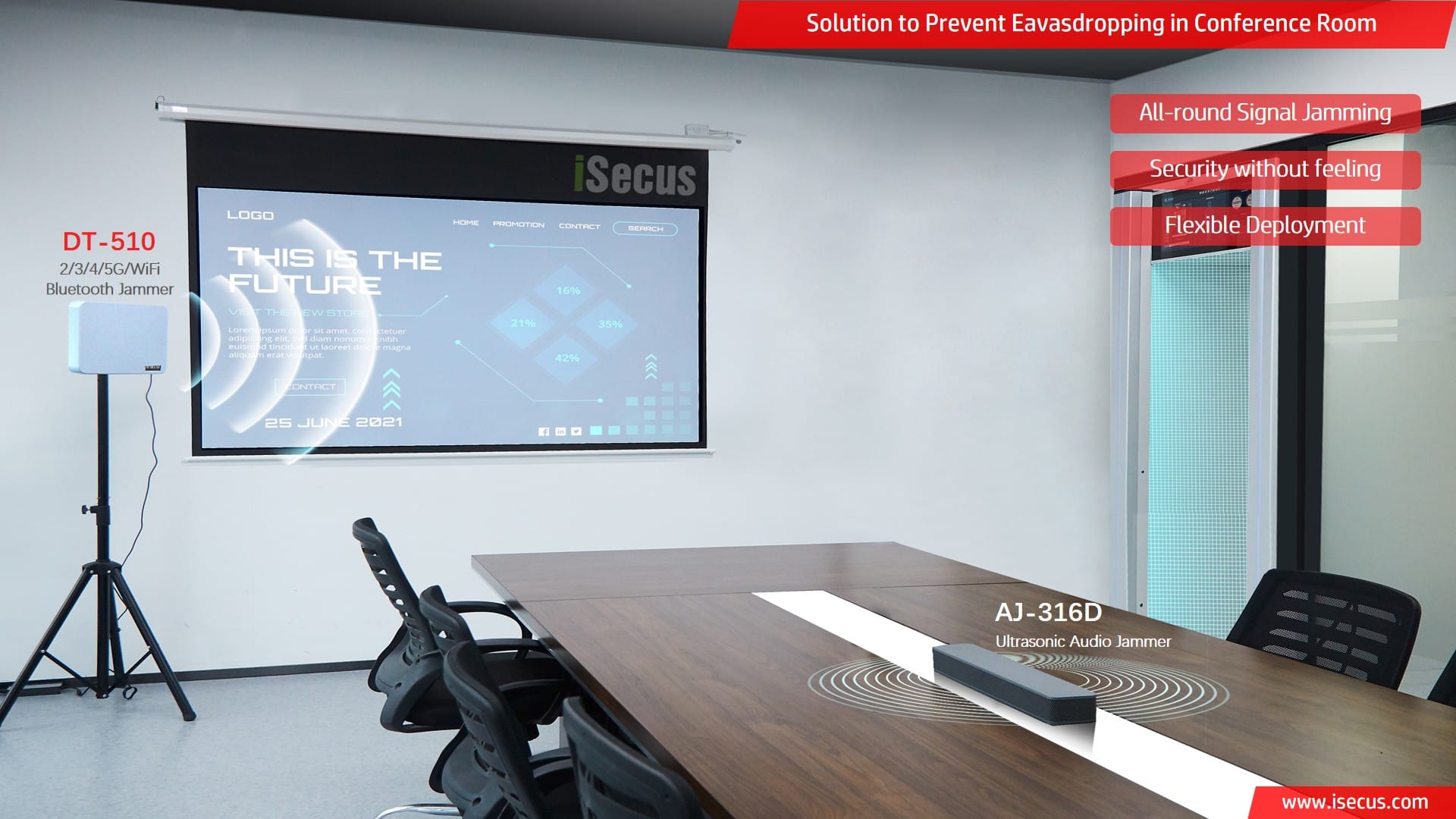
4. The Fundamental Difference Between Signal Jammers and Audio Jammers
Although both types of devices have “jamming” functions, their working principles and effects are completely different:
Signal Jammers
- Working Principle: Suppresses or interferes with wireless signals in the environment (2G-5G mobile signals, WiFi, Bluetooth, etc.)
- Effect: Prevents signal receiving devices in the environment from normal reception and communication
- Application Scenario: Prevents meeting content from being transmitted in real-time through wireless transmission devices
- Limitation: Cannot prevent local recording devices from functioning
Ultrasonic Audio Jammers
- Working Principle: Emits ultrasonic waves to create pulse impact interference on the microphones of recording devices
- Effect: Makes recorded sound become noise, making the actual content unidentifiable
- Application Scenario: Prevents on-site recording devices from effectively recording meeting content
- Limitation: Limited effectiveness on recording devices at a distance, coverage area is restricted
Comprehensive Application Strategy
In highly sensitive meetings, both types of devices should be used together: signal jammers block external information transmission, while ultrasonic audio jammers prevent local recording. Additionally, they should be combined with other detection equipment for comprehensive protection.
Building a Comprehensive Meeting Room Privacy Protection System
Having understood the characteristics of various anti-surveillance devices, we can construct a layered meeting room privacy protection system:
First Layer: Pre-meeting Detection
- Use wireless signal analyzers for environmental signal scanning
- Employ non-linear junction detectors to examine items in the meeting room
- Use wireless signal detectors for precise positioning in suspicious areas
Second Layer: Protection During Meetings
- Deploy signal jammers to block wireless communications
- Use audio jammers to prevent clear recording of sound
- Implement strict electronic device control policies
Third Layer: Regular Management
- Establish regular inspection mechanisms for meeting rooms
- Train employees to identify potential security threats
- Develop classified confidentiality systems to provide appropriate levels of protection for meetings of different sensitivity levels
Conclusion
In today’s increasingly important information security landscape, correctly understanding and using anti-surveillance equipment is a key element in protecting core business interests. Avoiding these common misconceptions can help you plan your security budget more effectively, choose appropriate device combinations, and establish a truly effective meeting room privacy protection system.
Remember, no single device can provide perfect security protection. True security comes from multi-layered, systematic protective measures and continuous security awareness cultivation.
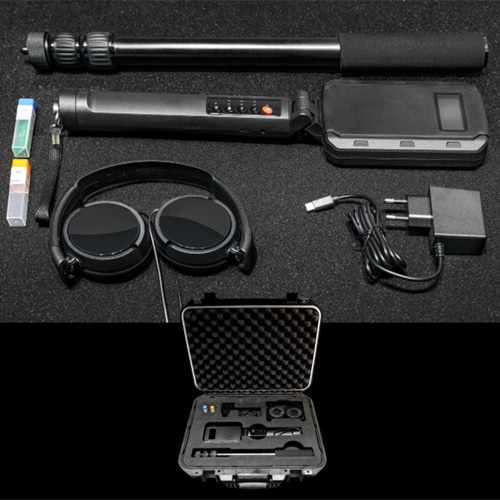
Some Popular TSCM Bug Sweeping Equipment from iSecus