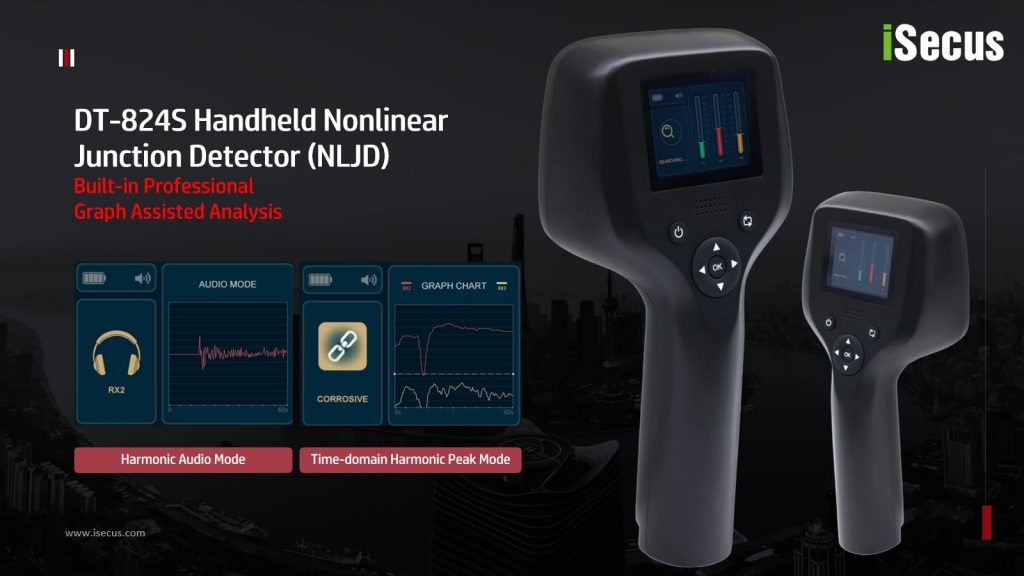
How to Select a Suitable Nonlinear Junction Detector NLJD?
In today’s world, where information security and privacy are significant and more concerned, NonLinear Junction Detector NLJDs have become indispensable TSCM equipment for detecting electronic devices, hidden cameras, or any unauthorized electronic surveillance equipment. Selecting the right NLJD is crucial to ensuring optimal performance and accuracy. This article will guide you through the critical factors to consider when choosing a suitable NLJD, focusing on frequency selection, power output, detection sensitivity, and why NLJDs sometimes struggle with cellphone detection.
Understanding NLJDs
Before diving into selection criteria, it’s essential to understand how non linear junction detectors work. NLJDs transmit a high-frequency signal into a target area, which interacts with semiconductor components found in electronic devices. These components produce harmonics (typically the second and third harmonic frequencies), which the detector captures and analyzes to identify the presence of electronic devices. NLJDs are widely used in counter-surveillance, security inspections, and law enforcement. For more information about the junction detection technology, please read our another post:
Counter-Surveillance Guide: Understanding Non-Linear Junction Detectors
Key Considerations for Selecting a Suitable NLJD
1. Frequency Selection
The operating frequency of an NLJD is one of its most crucial specifications. It determines the device’s ability to penetrate various materials and detect hidden electronics. Technically speaking, lower frequency, better penetration ability, provided the radio module performance without obvious difference.
Popular frequencies in the industry include: 900Mhz, 3.6Mhz, 2.4Ghz.
900 MHz: Offers good penetration through dense materials such as walls, wood, and concrete.Suitable for detecting electronics hidden in thicker or layered objects.
3.6 GHz: High sensitivity to smaller electronic components, making it ideal for detecting compact devices.Shorter penetration depth, which is advantageous for precise detection in smaller areas.
2.4 GHz:Provides a balance between penetration and sensitivity.Commonly used for detecting a wide range of electronic devices in diverse environments.More effective in moderately confined spaces while retaining sufficient penetration.
Choosing the right frequency depends on your specific needs. For general-purpose detection, 2.4 GHz is a versatile choice. For deeply hidden devices, 900 MHz may be better, while 3.6 GHz is excellent for pinpointing smaller electronics. This is not 100% assured that 800Mhz NLJD is better than 2.4Ghz concerning penetration ability, because each brands’ RF performance maybe varied. Sometimes, we may see, a 2.4GHz NLJD reaches better penetration performance on 800Mhz NLJD in a test scenario.
2. Power Output and Detection Sensitivity
The power output of an NLJD affects its ability to generate harmonics in the target electronics, while detection sensitivity determines its ability to capture weak harmonic signals.
Power Output: Higher power output enhances the range and penetration capability of the NLJD. Excessive power can cause interference, false positives, or damage to sensitive electronic components. Look for devices with adjustable power settings to fine-tune performance based on the environment.
Detection Sensitivity: High sensitivity is essential for detecting weak harmonic signals from small or low-powered electronic devices.Advanced NLJDs feature selective filtering to minimize noise and enhance detection accuracy.Ensure the detector can differentiate between second and third harmonics to reduce false alarms.
3. Portability and User Interface
An effective NLJD should be easy to operate and transport. Key features to look for include:
Ergonomic Design: Compact and lightweight models reduce user fatigue during extended operations.
Display and Indicators: Clear visual or auditory indicators for detecting harmonics, with an intuitive interface.
Battery Life: Long-lasting batteries or quick recharge options are vital for prolonged use in the field.
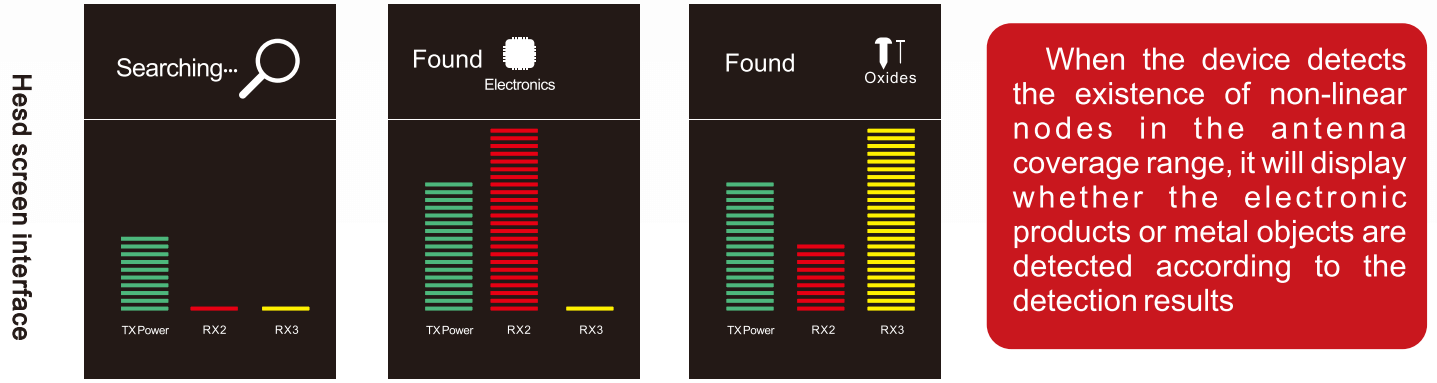
Additional Features to Consider
When selecting an NLJD, look for these advanced features that can enhance performance:
Adjustable Gain Control: Enables fine-tuning of sensitivity to minimize false positives.
Data Logging: Allows you to record detection results for further analysis or reporting.
Multi-Frequency Operation: Some NLJDs can switch between multiple frequencies to adapt to different scenarios.
Built-in Filters: High-quality filters can reduce interference from ambient RF signals.
Why NLJD Detecting Performance on Cellphones May Not Be Optimal?
One of the challenges often encountered with NLJDs is their limited performance when detecting cellphones. Here are a few reasons:
Complex Construction: Modern smartphones use highly integrated circuits with minimal exposed junctions. These designs produce weaker harmonic signals, making detection more challenging.
Shielding Materials: Smartphones often contain shielding to reduce electromagnetic interference, which also diminishes harmonic generation.
Low Emission of Non-Linear Signals: In standby mode, many smartphones have circuits that are either inactive or operate at low power, further reducing detectable harmonics.
Ambient Noise Interference: Urban environments with numerous RF signals can mask the weak harmonics emitted by smartphones, complicating detection.
Conclusion
Choosing the right NLJD requires careful consideration of factors such as frequency selection, power output, detection sensitivity, and the specific challenges associated with detecting certain devices like smartphones. By understanding these aspects and aligning them with your operational requirements, you can select an NLJD that meets your needs effectively. Investing in a high-quality NLJD not only enhances your ability to detect hidden electronics but also ensures the safety and security of your environment.
Global NLJD Manufacturing: Key Players and Market Insights
Non-linear junction detectors (NLJDs) are advanced devices designed to identify concealed electronic circuits, playing a critical role in security operations. Their reliance on cutting-edge technology limits production to a select few nations with specialized expertise. Currently, Russia, USA, China, and the UK. lead global NLJD manufacturing, leveraging their technological infrastructure to meet demand from defense, law enforcement, and security sectors.
As electronic surveillance threats escalate, these countries remain pivotal suppliers, driving innovation and maintaining dominance in this niche yet vital market. Their strategic capabilities ensure ongoing advancements in NLJD technology, addressing evolving security challenges worldwide.
Comparisons Chart of The Nonlinear Junction Detector NLJDs in the Worldwide Market
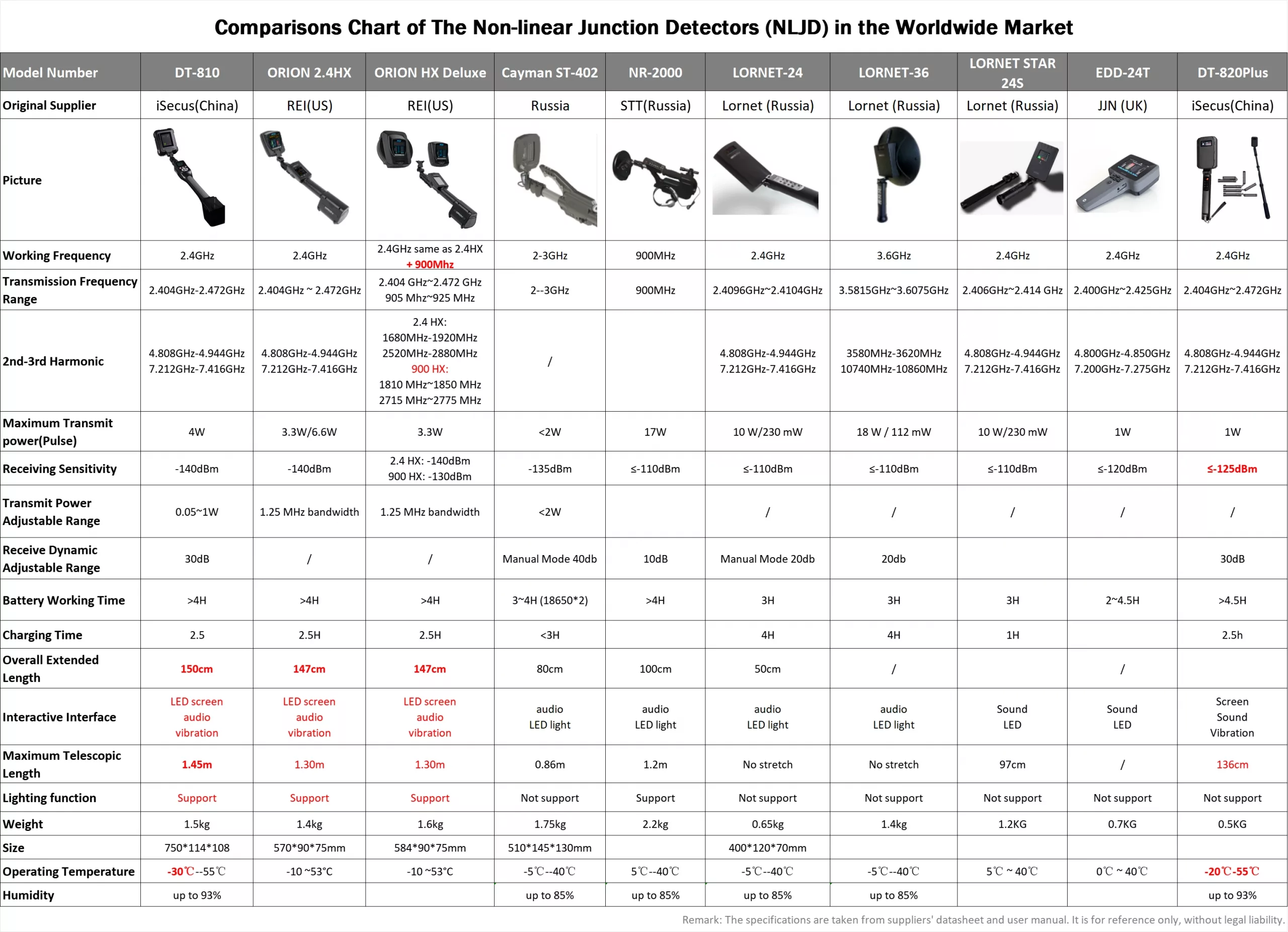
| Model Number | DT-810 | ORION 2.4HX | ORION HX Deluxe | Cayman ST-402 | NR-2000 | LORNET-24 | LORNET-36 | LORNET STAR 24S | EDD-24T | DT-820Plus |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Original Supplier | iSecus(China) | REI(US) | REI(US) | Russia | STT(Russia) | Lornet (Russia) | Lornet (Russia) | Lornet (Russia) | JJN (UK) | iSecus(China) |
| Working Frequency | 2.4GHz | 2.4GHz | 2.4GHz same as 2.4HX + 900Mhz | 2-3GHz | 900MHz | 2.4GHz | 3.6GHz | 2.4GHz | 2.4GHz | 2.4GHz |
| Transmission Frequency Range | 2.404GHz~2.472GHz | 2.404GHz ~ 2.472GHz | 2.404 GHz~2.472 GHz 905 Mhz~925 MHz | 2--3GHz | 900MHz | 2.4096~2.4104GHz | 3.5815~3.6075GHz | 2.406~2.414 GHz | 2.400~2.425GHz | 2.404~2.472GHz |
| 2nd-3rd Harmonic | 4.808GHz~4.944GHz 7.212GHz~7.416GHz | 4.808GHz~4.944GHz 7.212GHz~7.416GHz | 2.4 HX: 2.4GHz same as 2.4HX 900 HX: 1810~1850 MHz 2715~2775 MHz | / | 4.808~4.944GHz 7.212~7.416GHz | 3580~3620MHz 10740~10860MHz | 4.808~4.944GHz 7.212~7.416GHz | 4.800~4.850GHz 7.200~7.275GHz | 4.808~4.944GHz 7.212~7.416GHz |
|
| Maximum Transmit power(Pulse) | 4W | 3.3W/6.6W | 3.3W | <2W | 17W | 10 W/230 mW | 18 W / 112 mW | 10 W/230 mW | 1W | 1W |
| Receiving Sensitivity | -140dBm | -140dBm | 2.4 HX: -140dBm 900 HX: -130dBm | -135dBm | ≤-110dBm | ≤-110dBm | ≤-110dBm | ≤-110dBm | ≤-120dBm | ≤-125dBm |
| Transmit Power Adjustable Range | 0.05~1W | 1.25 MHz bandwidth | 1.25 MHz bandwidth | <2W | / | / | / | / | / | |
| Receive Dynamic Adjustable Range | 30dB | / | / | Manual Mode 40db | 10dB | Manual Mode 20db | 20db | 30dB | ||
| Battery Working Time | >4H | >4H | >4H | 3~4H (18650*2) | >4H | 3H | 3H | 3H | 2~4.5H | >4.5H |
| Charging Time | 2.5 | 2.5H | 2.5H | <3H | 4H | 4H | 1H | 2.5h | ||
| Overall Extended Length | 150cm | 147cm | 147cm | 80cm | 100cm | 50cm | / | / | ||
| Interactive Interface | LED screen audio vibration | LED screen audio vibration | LED screen audio vibration | audio LED light | audio LED light | audio LED light | audio LED light | Sound LED | Sound LED | Screen Sound Vibration |
| Maximum Telescopic Length | 1.45m | 1.30m | 1.30m | 0.86m | 1.2m | No stretch | No stretch | 97cm | / | 136cm |
| Lighting function | Support | Support | Support | Not support | Support | Not support | Not support | Not support | Not support | Not support |
| Weight | 1.5kg | 1.4kg | 1.6kg | 1.75kg | 2.2kg | 0.65kg | 1.4kg | 1.2KG | 0.7KG | 0.5KG |
| Size | 750*114*108 | 570*90*75mm | 584*90*75mm | 510*145*130mm | 400*120*70mm | |||||
| Operating Temperature | -30℃--55℃ | -10 ~53°C | -10 ~53°C | -5℃--40℃ | 5℃--40℃ | -5℃--40℃ | -5℃--40℃ | 5℃ ~ 40℃ | 0℃ ~ 40℃ | -20℃-55℃ |
| Humidity | up to 93% | up to 85% | up to 85% | up to 85% | up to 85% | up to 93% | ||||
| Remark: The specifications are taken from suppliers' datasheet and user manual. It is for reference only, without legal liability. | ||||||||||
FAQ related to Nonliner Junction Detector NLJDs?
1). What can non-linear junction detectors find?
- Answer: NLJDs are designed to detect hidden electronic devices by identifying non-linear junctions, which can be found in:
- Semiconductors (like transistors and diodes)
- Electronic components in surveillance devices
- Passive components like capacitors and resistors
- Even certain types of metal-to-metal junctions or corrosion
2). Are non-linear junction detectors legal to use?
- Answer: The legality of using NLJDs varies by jurisdiction. In many countries, they are legal for personal use but might require authorization for commercial or law enforcement applications. Always check local laws, especially regarding the use in public or private spaces without consent.
3). How do nonlinear junction detector NLJD differentiate between electronics and other metal objects?
- Answer: NLJDs emit a radio frequency signal and listen for harmonics or other non-linear responses that indicate the presence of semiconductor junctions. Metal objects typically respond linearly to the signal, whereas electronic devices produce harmonic frequencies.
4). Can nonlinear junction detector nlljd detect through walls?
- Answer: Yes, but the effectiveness depends on the material of the wall and the sensitivity of the NLJD. Thick concrete or metal barriers can significantly reduce the range, while drywall or wood might be less obstructive.
5). What are the limitations of non-linear junction detectors?
- Answer:
- False Positives: They can detect any non-linear junction, which might include innocuous items like corroded metals or some types of jewelry.
- Range: The detection range is limited and can be affected by the environment.
- Training: Requires trained operators to interpret results correctly.
- Interference: Electronic noise from other sources can interfere with detection.
6). How to use non-linear junction detectors effectively?
- Answer:
- Scan Slowly: Move the NLJD slowly to ensure thorough coverage.
- Use Headphones: To better hear the audio feedback.
- Check from Multiple Angles: Electronics might be hidden in unusual places.
- Verify with Visual Inspection: If a signal is detected, visually inspect the area for suspicious objects.