Counter-Surveillance Guide: Understanding Non-Linear Junction Detectors
| Key Points Table |
|---|
| 1. Introduction to Non-Linear Junction Detectors |
| 2. How Non-Linear Junction Detectors Work |
| 3. Applications of Non-Linear Junction Detectors (NLJDs) |
| 4. Key Features and Specifications of Non-Linear Junction Detectors |
| 5. Popular Non-linear Junction Detectors in the worldwide market |
| 6. FAQ related to NLJDs |
1. Introduction to Non-Linear Junction Detectors
What is a Non-Linear Junction Detector?
Non-linear junction detectors (NLJDs) are advanced tools designed to uncover the presence of electronic devices that might be hidden or concealed in walls, floors, ceilings, lamps, books, furniture or containers. No matter whether these electronic devices are power on or power off. Unlike traditional metal detectors, NLJDs can differentiate between electronic components and other metallic objects, making them invaluable for
- Security Professionals seeking to ensure the privacy of sensitive meetings or secure environments.
- Individuals who want to protect their personal spaces from unauthorized surveillance.
The Science Behind NLJD Technology
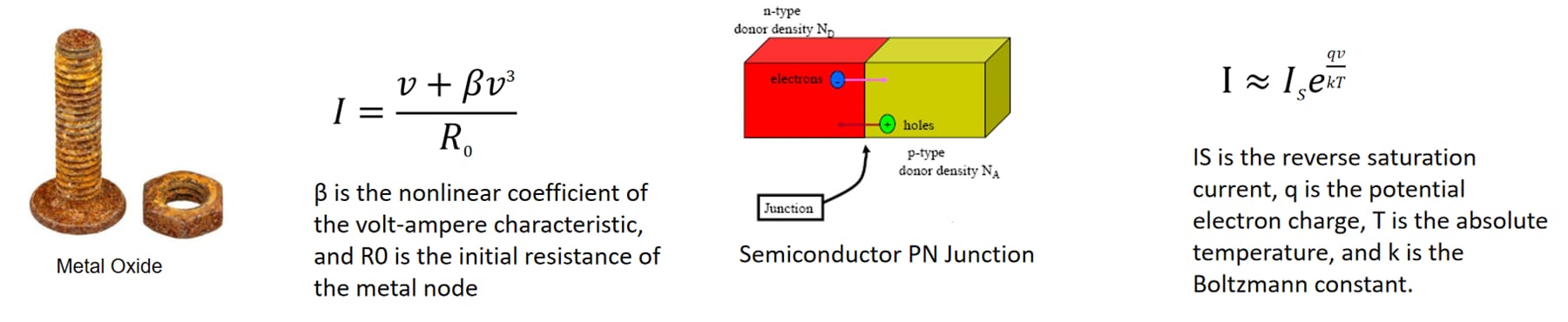
Nonlinear Junction Introduction
According to the relationship between received signal frequency and transmitted signal frequency, Radar is divided into fundamental wave radar and harmonic radar. Nonlinear junction detector is considered harmonic radars.
Natural objects generally do not have the ability to re-radiate harmonics, such as mountains, oceans, land, etc., and purely man-made objects such as metal blocks will not produce harmonic radiation. Only the place where two metals combine to produce oxides (MOM) will produce harmonic radiation. Wave radiation, the most representative is the metal oxide and semiconductor PN junction. Due to this characteristic, NLJD is used to detect various electronic devices, explosive electronic control devices, eavesdropping devices, recording devices, etc. It finds wide applications in fields such as public security and confidentiality.
(Note: After two metals of the same or dissimilar type are in contact, a metal node is formed when there is an appropriate pressure, distance, or a layer of oxide is formed in the middle. The volt-ampere characteristics of the metal node and the PN junction are different.)
Non-Linear Junctions Detection Technology Introduction
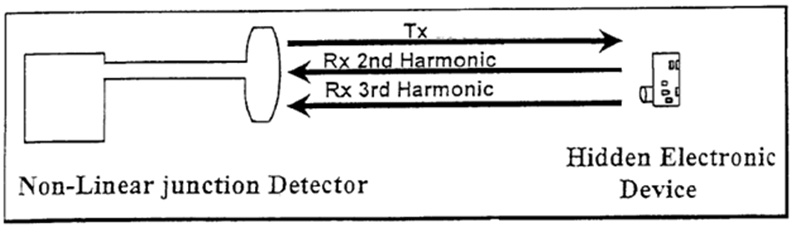
At the heart of NLJD technology is the ability to detect non-linear responses from electronic junctions. Here’s how:
- Signal Transmission: The NLJD emits a continuous or pulsed RF signal.
- Non-Linear Response: When this signal encounters a non-linear junction, it produces harmonic frequencies or other non-linear signals.
- Detection: The device then listens for these harmonics, indicating the presence of an electronic device.
This technology leverages the fact that electronic components like diodes, transistors, and even corroded metals produce unique signatures when exposed to RF signals, allowing NLJDs to pinpoint hidden electronics.
2. How Non-Linear Junction Detectors Work
Principles of Operation
- RF Signal Emission: NLJDs emit a radio frequency signal at a specific frequency. The latest popular frequency range is 404GHz-2.472GHz, and800-900 MHz.
- Non-Linear Response Detection: The device listens for harmonics or inter-modulation products. Electronics typically produce second and third harmonics, which are key indicators of their presence.
- Differentiation: The detector differentiates between linear responses from metals and non-linear responses from electronics, providing precise detection capabilities.
Types of Junctions Detected
- Semiconductor Junctions: The most common type, found in every electronic device, including:
- Diodes
- Transistors
- Integrated Circuits
- Passive Electronic Components: These can also create non-linear junctions:
- Capacitors
- Resistors
- Inductors
- Other Non-Linear Junctions: Less common but detectable:
- Rust or corrosion on metal objects
- Certain metal-to-metal contacts or alloys
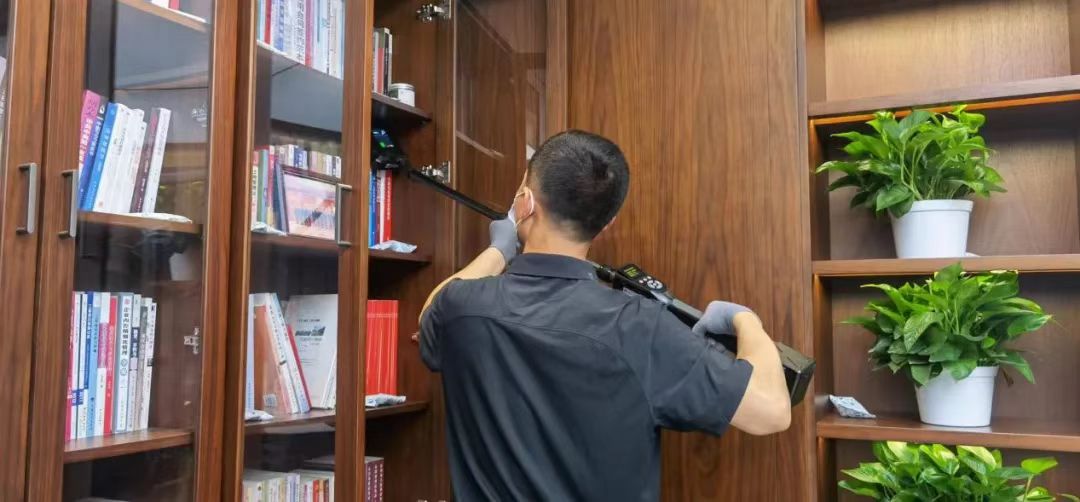
3. Applications of Non-Linear Junction Detectors (NLJDs)
NLJD is an instrument that applies the non-linear scattering principle of semiconductor PN junctions to detect and locate electronic contraband by detecting the harmonics scattered by the target junction. The non-linear node detector first appeared in the 1960s-1970s, initially used by the US military to detect metallic targets such as buried landmines. Countries such as the UK and Russia have also conducted in-depth research in this field soon later. There are wide applications of non-linear junction detectors:
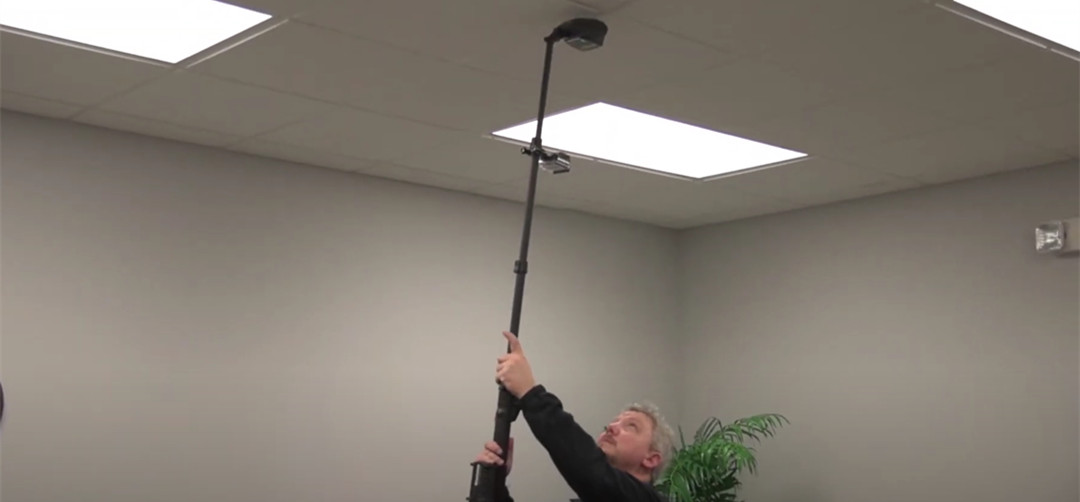
Counter-Surveillance
- Bug Sweeps: Non-liear Junction Detectors are vital for sweeping areas for hidden microphones, cameras, or GPS trackers. They are used:
- Before sensitive meetings or negotiations
- In executive offices or boardrooms
- During high-profile events where privacy is critical
Electronic Bug Detection
- Government and Military: Agencies use NLJDs to:
- Secure classified information
- Ensure safe communication channels
- Detect potential espionage devices in sensitive locations
- Law Enforcement: Detecting hidden recording devices or trackers during investigations or to protect witnesses.
Homeland Security and Law Enforcement
- Border Control: Non-linear junction detectors are used to check vehicles or luggage for hidden electronics, potentially uncovering smuggling or terrorist activities.
- Anti-Terrorism: They play a role in detecting components of IEDs or communication devices used by terrorists.
- Critical Infrastructure Protection: Ensuring no unauthorized surveillance or sabotage devices are present in key facilities like power plants or data centers.
- Personal Security:
- Privacy Protection: Individuals use NLJDs to scan their homes or offices for hidden cameras or bugs.
- Travel Security: Checking hotel rooms or rental cars for hidden devices before settling in.
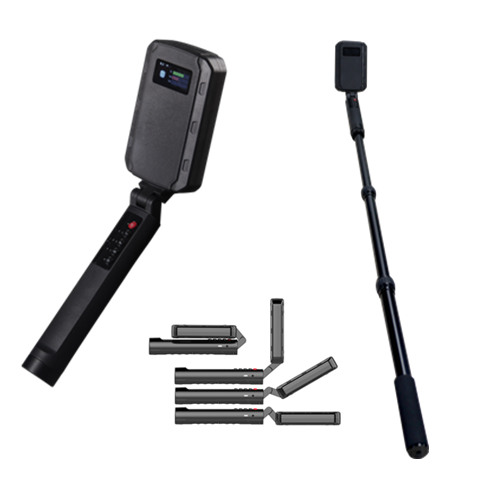
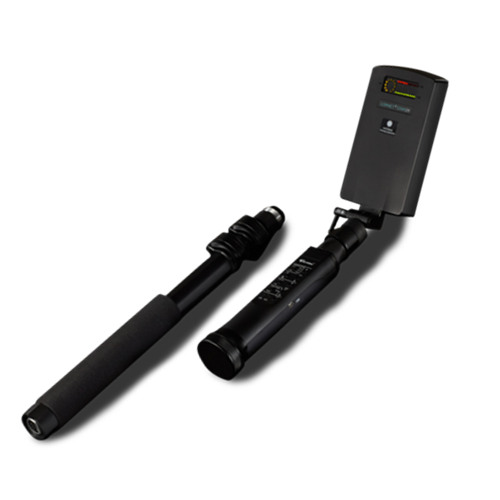
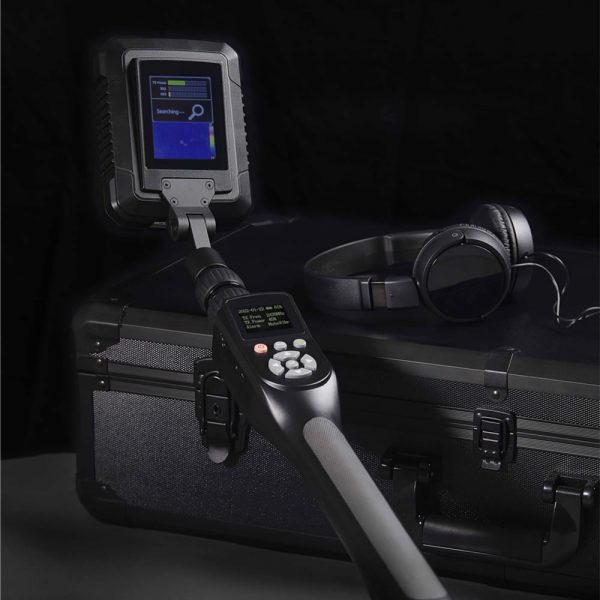
4. Key Features and Specifications of Non-Linear Junction Detectors
NLJDs are specialized tools designed to detect semiconductor components in electronic devices, even if the devices are powered off or hidden. This chapter provides an in-depth look at the critical features and specifications that define NLJDs, including frequency bands and power output, sensitivity, portability and ease of use.
Frequency Bands
- Operating Frequency: NLJDs typically operate in the 2.4 GHz band which is the main-trend adopted by USA/European/Chinese suppliers. Russian brands such as Lornet still offer 900Mhz bands. Below are the advantages of 2.4G:
- Effective Penetration: This frequency can penetrate through various non-metallic materials, making it suitable for detecting hidden electronics behind walls or barriers.
- Detection Capability: Ideal for identifying electronic components like semiconductor junctions in devices.
- Interference Management: The 2.4 GHz band is less likely to interfere with other electronic signals, ensuring the NLJD can function effectively in environments with existing RF activity.
Power Output
- Adjustable Power: Many NLJDs feature adjustable power settings, which allow:
- Environment Adaptation: Operators can adjust the power to match the search environment, balancing between detection range and battery life.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensures the device can be used within legal power emission limits.
- Efficiency: Higher power settings can extend detection range but might reduce battery life, so users can optimize for their specific needs.
Receiving Sensitivity
- Detection Precision: Receiver sensitivity refers to the ability of the NLJD’s receiving system to detect weak signals or harmonics generated by non-linear junctions. High sensitivity is crucial for:
- Identifying Small Components: Detecting semiconductor junctions, even when unpowered, along with passive electronic components.
- Minimizing False Positives: Advanced signal processing reduces the likelihood of false alarms, ensuring accurate detection.
Portability
- Compact Design: NLJDs are designed to be:
- Portable: Small enough to be easily transported, suitable for mobile security operations.
- Lightweight: Typically weighs between 2 to 3 kg, ensuring ease of handling during extended searches.
Ease of Use
- User-Friendly Interface:
- Intuitive Controls: Simple controls for power, sensitivity, and mode selection, minimizing the learning curve for operators.
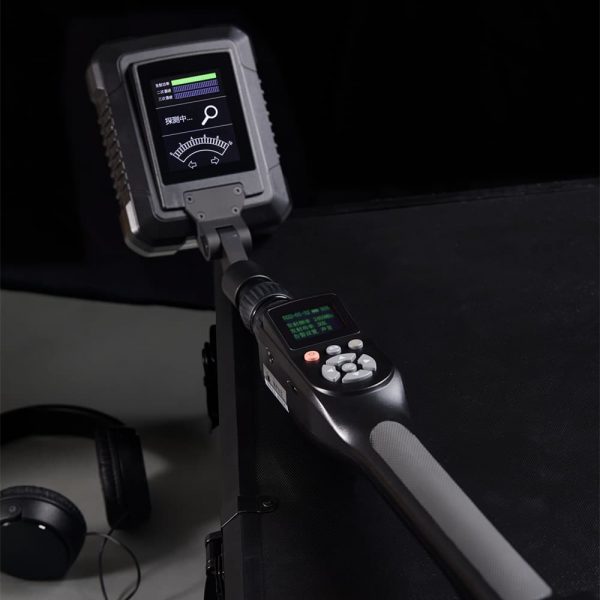
- LED Display: Provides clear visual feedback on signal strength, battery life, and harmonic detection, aiding in precise detection.
- Audio Feedback: Headphone jack allows operators to listen to audio cues, which can be crucial for locating electronic devices in noisy environments.
- Ergonomic Design:
- Comfortable Handling: Designed for prolonged use, reducing operator fatigue during long sweeps.
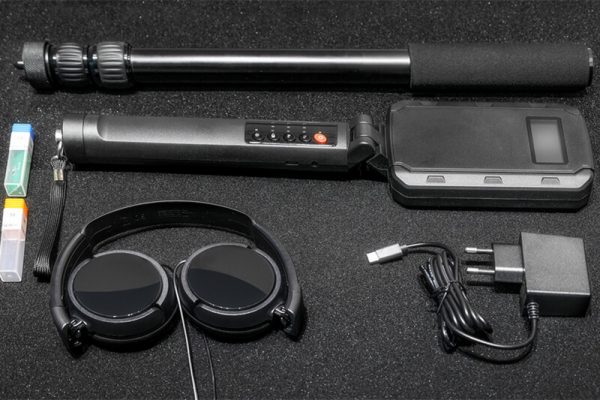
- Adjustable Antenna: Allows for scanning in tight spaces or around corners, enhancing the device’s versatility.
- Battery Life:
- Long-Lasting: Many NLJDs offer up to 8 hours of continuous operation on a single charge, allowing for extended use without frequent recharging.
- Rechargeable: Comes with rechargeable batteries, reducing operational costs and environmental impact.
- Calibration:
- Automatic Calibration: Some models include auto-calibration features to adapt to different environments, ensuring consistent performance.
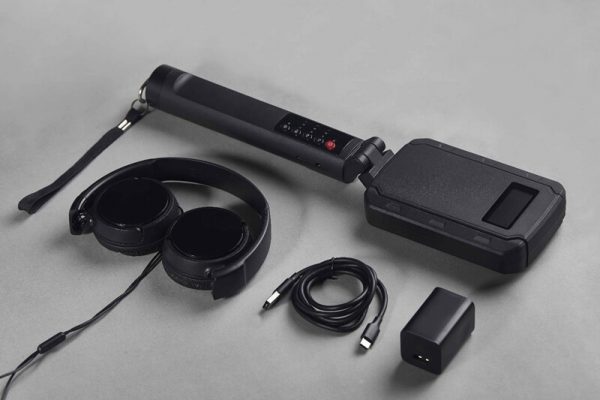
- Accessories:
- Carrying Case: Typically provided for protection during transport.
- Headphones: Included for audio feedback, enhancing detection accuracy.
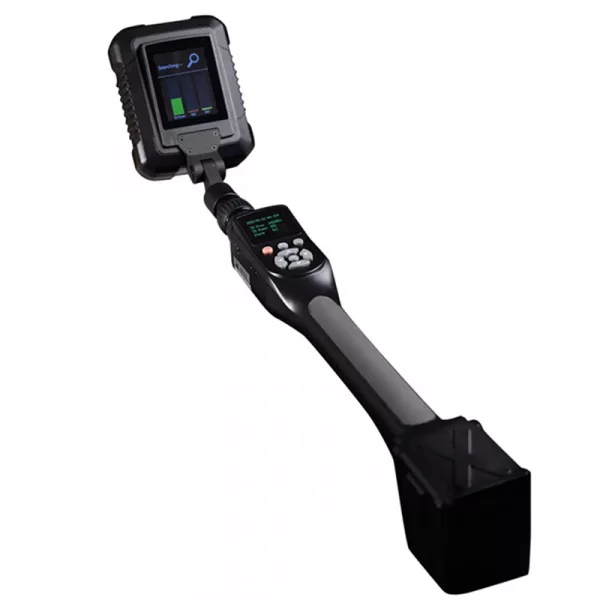
5. Popular Non-linear Junction Detectors in the worldwide market.
NLJDs is a very niche market. By now, the original manufacturers in the world are mainly coming from United States, Russia, United Kingdom, China, Israel, etc. Here some popular NLJD models are listed below with a general comparison on the configuration.
Model
Brand
Frequency
Receiving Sensitivity
Power Consumption
Operating Time(Pulse)
Alarm
Extendable Pole
Equipment Body Weight
Working Environment
DT-820Plus
iSecus (China)
2.404GHz – 2.472GH
≤-125dBm
1W (Max.)
≥4.5H
Screen Alert, Sound, Vibration
80-136cm Extendable
0.5KG (Without Rod)
-20℃-55℃
Star24
Lornet(Russia)
2.406GHz – 2.414GHz
≤-110dBm
10w
3H
Screen Alert, Sound
43-97cm Extendable
1.0 KG (Without Rod)
5℃-40℃
EDD-24T
JJN Digital(UK)
2.400 GHZ to 2.425 GHz
≤-120dBm
1W
4.5H
Screen Alert, Sound
None
0.7KG
-0℃-50℃
Model
Brand
Frequency
Receiving Sensitivity
Power Consumption
Operating Time(Pulse)
Alarm
Extendable Pole
Lighting function
Equipment Body Weight
Working Environment
DT-810
iSecus (China)
2.404GHz – 2.472GH
≤-140dBm
4W (Max.)
≥4H
Screen Alert, Sound, Vibration
145cm Extendable
Supported
1.5KG
-30℃-55℃
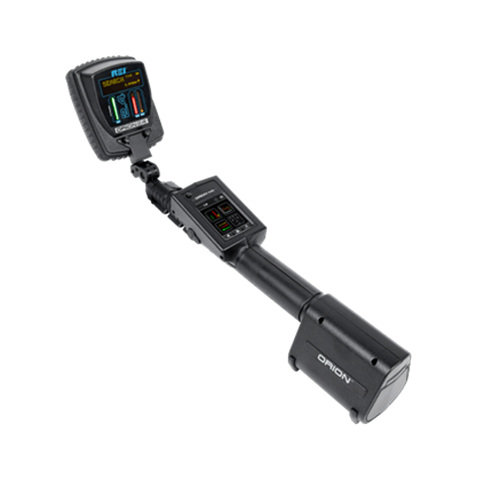
Orion2.4HX
REI (USA)
2.404GHz – 2.472GH
≤-140dBm
3.3W/6.6W
≥4H
Screen Alert, Sound, Vibration
130cm Extendable
Supported
1.4KG
-10℃-55℃
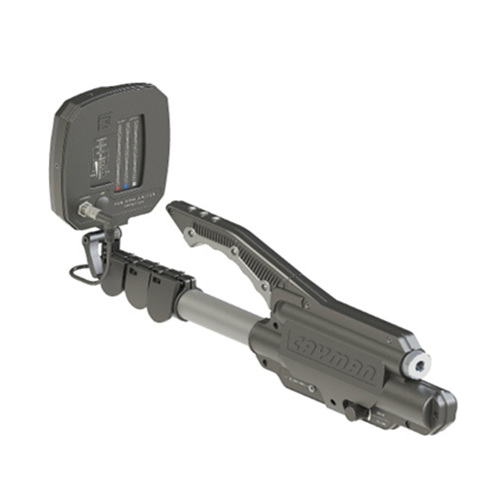
ST-402
Cayman (Russia)
2-3GHz
≤-140dBm
2W
3-4H
Screen Alert, Sound
86cm Extendable
NOT Supported
1.7KG
5℃-40℃
6. FAQ related to NLJDs?
1). What can non-linear junction detectors find?
- Answer: NLJDs are designed to detect hidden electronic devices by identifying non-linear junctions, which can be found in:
- Semiconductors (like transistors and diodes)
- Electronic components in surveillance devices
- Passive components like capacitors and resistors
- Even certain types of metal-to-metal junctions or corrosion
2). Are non-linear junction detectors legal to use?
- Answer: The legality of using NLJDs varies by jurisdiction. In many countries, they are legal for personal use but might require authorization for commercial or law enforcement applications. Always check local laws, especially regarding the use in public or private spaces without consent.
3). How do non-linear junction detectors differentiate between electronics and other metal objects?
- Answer: NLJDs emit a radio frequency signal and listen for harmonics or other non-linear responses that indicate the presence of semiconductor junctions. Metal objects typically respond linearly to the signal, whereas electronic devices produce harmonic frequencies.
4). Can non-linear junction detectors detect through walls?
- Answer: Yes, but the effectiveness depends on the material of the wall and the sensitivity of the NLJD. Thick concrete or metal barriers can significantly reduce the range, while drywall or wood might be less obstructive.
5). What are the limitations of non-linear junction detectors?
- Answer:
- False Positives: They can detect any non-linear junction, which might include innocuous items like corroded metals or some types of jewelry.
- Range: The detection range is limited and can be affected by the environment.
- Training: Requires trained operators to interpret results correctly.
- Interference: Electronic noise from other sources can interfere with detection.
6). How to use non-linear junction detectors effectively?
- Answer:
- Scan Slowly: Move the NLJD slowly to ensure thorough coverage.
- Use Headphones: To better hear the audio feedback.
- Check from Multiple Angles: Electronics might be hidden in unusual places.
- Verify with Visual Inspection: If a signal is detected, visually inspect the area for suspicious objects.
7). Can we use NLJD in vehicles to find hidden eavasdropping devices?
- Answer: Technically speaking, Yes. However, in real-world experience, NLJDs are too unreliable for vehicle bug detection due to excessive false alarms, because there are too many electronic components in the vehicles. RF scanners, thermal imaging, and physical inspections are far more effective.
8). When choosing NLJD, which frequency is the best among 900Mhz, 2.4G and 3.6G?
- Answer: Choosing the right frequency depends on your specific needs. For general-purpose detection, 2.4 GHz is a versatile choice. For deeply hidden devices, 900 MHz may be better, while 3.6 GHz is excellent for pinpointing smaller electronics. This is not 100% assured that 800Mhz NLJD is better than 2.4Ghz concerning penetration ability, because each brands’ RF performance maybe varied. Besides, power output, receiving sensitivity, detection algorithm also affect the NLJD’s working performance. Sometimes, we may see, a 2.4GHz NLJD reaches better penetration performance on 800Mhz NLJD in a test scenario.
- Here is a general guide not strictly, more importantly it depends on your detection scenario:
- General use: 2.4 GHz (balances range and sensitivity for most bugs).
- Deep penetration: 900 MHz (better for shielded/hidden devices).
- Precision detection: 3.6 GHz (ideal for tiny electronics).